All Categories
Featured
Table of Contents
Tax obligation lien investing can provide your profile exposure to realty all without needing to in fact own building. Professionals, nevertheless, claim the procedure is complicated and advise that amateur investors can conveniently get burned. Below's every little thing you need to find out about buying a tax lien certificate, including exactly how it functions and the risks entailed.
The notification typically comes before harsher activities, such as a tax levy, where the Internal Earnings Solution (IRS) or local or metropolitan governments can really take somebody's home to recoup the debt. A tax lien certification is produced when a residential property owner has actually fallen short to pay their taxes and the city government concerns a tax obligation lien.
Tax lien certificates are typically auctioned off to investors looking to revenue. To recoup the overdue tax obligation dollars, municipalities can then market the tax obligation lien certification to private financiers, who care for the tax costs in exchange for the right to collect that cash, plus passion, from the homeowner when they eventually pay back their equilibrium.
How To Invest In Tax Liens
allow for the transfer or project of overdue property tax liens to the economic sector, according to the National Tax Obligation Lien Organization, a nonprofit that represents federal governments, institutional tax lien investors and servicers. Here's what the process looks like. Tax lien capitalists need to bid for the certification in a public auction, and how that process functions depends upon the details town.
Call tax obligation authorities in your location to ask how those overdue taxes are accumulated. Auctions can be on the internet or personally. In some cases winning quotes most likely to the investor prepared to pay the most affordable rate of interest rate, in a technique called "bidding down the interest price." The community develops an optimum rate, and the bidder offering the lowest rate of interest underneath that optimum wins the public auction.
The winning prospective buyer has to pay the whole tax obligation costs, consisting of the delinquent debt, interest and fines. The investor has to wait up until the building proprietors pay back their whole equilibrium unless they do not.
While some capitalists can be awarded, others could be caught in the crossfire of complex regulations and loopholes, which in the worst of scenarios can result in hefty losses. From a simple earnings standpoint, many capitalists make their cash based on the tax lien's interest rate. Rates of interest differ and depend upon the jurisdiction or the state.
Earnings, nonetheless, do not constantly amount to yields that high during the bidding process. Ultimately, the majority of tax obligation liens purchased at auction are sold at prices between 3 percent and 7 percent country wide, according to Brad Westover, executive supervisor of the National Tax Obligation Lien Association. Before retiring, Richard Rampell, previously the president of Rampell & Rampell, an accountancy firm in Hand Beach, Florida, experienced this firsthand.
Tax Liens Investment
Then huge institutional investors, including financial institutions, hedge funds and pension funds, chased after those greater yields in auctions around the country. The larger investors aided bid down interest prices, so Rampell's group had not been making considerable money any longer on liens.
That rarely takes place: The tax obligations are generally paid before the redemption date. Liens likewise are initial eligible repayment, also prior to home mortgages. Even so, tax obligation liens have an expiry date, and a lienholder's right to confiscate on the residential property or to gather their financial investment expires at the very same time as the lien.
"In some cases it's six months after the redemption duration," Musa claims. "Do not think you can just get and neglect concerning it." Private capitalists who are thinking about financial investments in tax liens should, most importantly, do their homework. Experts suggest avoiding residential or commercial properties with ecological damage, such as one where a gas terminal unloaded hazardous product.
How Does Investing In Tax Liens Work
"You need to truly comprehend what you're purchasing," claims Richard Zimmerman, a companion at Berdon LLP, a bookkeeping firm in New york city City. "Understand what the home is, the neighborhood and values, so you do not buy a lien that you will not have the ability to accumulate." Potential investors ought to also take a look at the building and all liens against it, as well as current tax obligation sales and price of comparable properties.
Keep in mind that the information you find can commonly be obsoleted. "Individuals get a list of residential or commercial properties and do their due diligence weeks before a sale," Musa states. "Half the residential or commercial properties on the listing may be gone since the taxes get paid. You're squandering your time. The closer to the date you do your due persistance, the much better.
How To Invest In Tax Liens
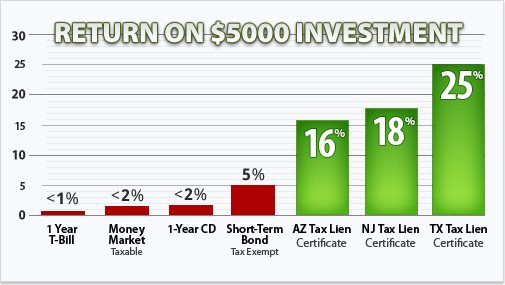
Westover states 80 percent of tax obligation lien certifications are marketed to members of the NTLA, and the firm can frequently pair up NTLA members with the best institutional financiers. That might make handling the process less complicated, especially for a novice. While tax lien financial investments can provide a generous return, recognize the fine print, information and rules.
"However it's made complex. You have to understand the information." Bankrate's contributed to an upgrade of this tale.
Residential property tax obligation liens are an investment niche that is overlooked by the majority of financiers. Buying tax liens can be a lucrative though relatively risky business for those who are knowledgeable concerning realty. When individuals or services stop working to pay their real estate tax, the municipalities or various other federal government bodies that are owed those taxes put liens versus the residential properties.
Best States For Tax Lien Investing
These claims on security are additionally exchanged amongst investors that wish to create above-average returns. With this procedure, the community obtains its tax obligations and the capitalist gets the right to collect the amount due plus rate of interest from the borrower. The procedure hardly ever finishes with the financier confiscating ownership of the residential property.
Liens are cost public auctions that occasionally involve bidding battles. If you need to confiscate, there may be other liens versus the residential or commercial property that keep you from taking ownership. If you get the residential property, there may be unexpected expenditures such as repair work and even kicking out the existing occupants. You can likewise invest indirectly through home lien funds.
It properly links up the residential property and avoids its sale until the owner pays the taxes owed or the property is seized by the financial institution. When a landowner or homeowner falls short to pay the taxes on their building, the city or region in which the home is located has the authority to place a lien on the residential property.
Residential or commercial property with a lien connected to it can not be offered or re-financed up until the taxes are paid and the lien is removed. When a lien is released, a tax lien certification is developed by the district that mirrors the quantity owed on the residential or commercial property plus any type of interest or penalties due.

It's approximated that an added $328 billion of residential or commercial property taxes was analyzed throughout the U.S. in 2021. It's tough to evaluate nationwide property tax lien numbers.
Latest Posts
Tax Repossessed Property
How To Do Tax Lien Investing
Investing In Tax Lien Certificates For Beginners